The first contact between the people who inhabited the remote areas of Eurasia took place in prehistory. In later periods, various products found their way from East to West and vice versa. In addition to artifacts, materials, resources, animals and plants, the exchange of ideas, knowledge and experiences, human migration, but also the transmission of various pathogens were significant. The most famous route or the network of roads connected east and west of Eurasia was called the Silk Road. The name Silk Road (Seidenstraße) was coined by the German geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen in the second half of the 19th century. […]
The capital of China is Beijing which means Northern Capital (bei-jing) and has been in contrast to Southern Capital (nan-jing) or Nanjing. The first humans have lived here from 700 000 to 200 000 years ago and this human type is known as Peking man (Homo erectus pekinesis). On the site of Zhoukoudian near Beijing were found around 40 human remains and this location is founding point of human settlement in the Beijing region. During the time, Beijing has changed its importance up to the 15th century and the dynasty of Ming when becomes imperial capital. The Chinese education system
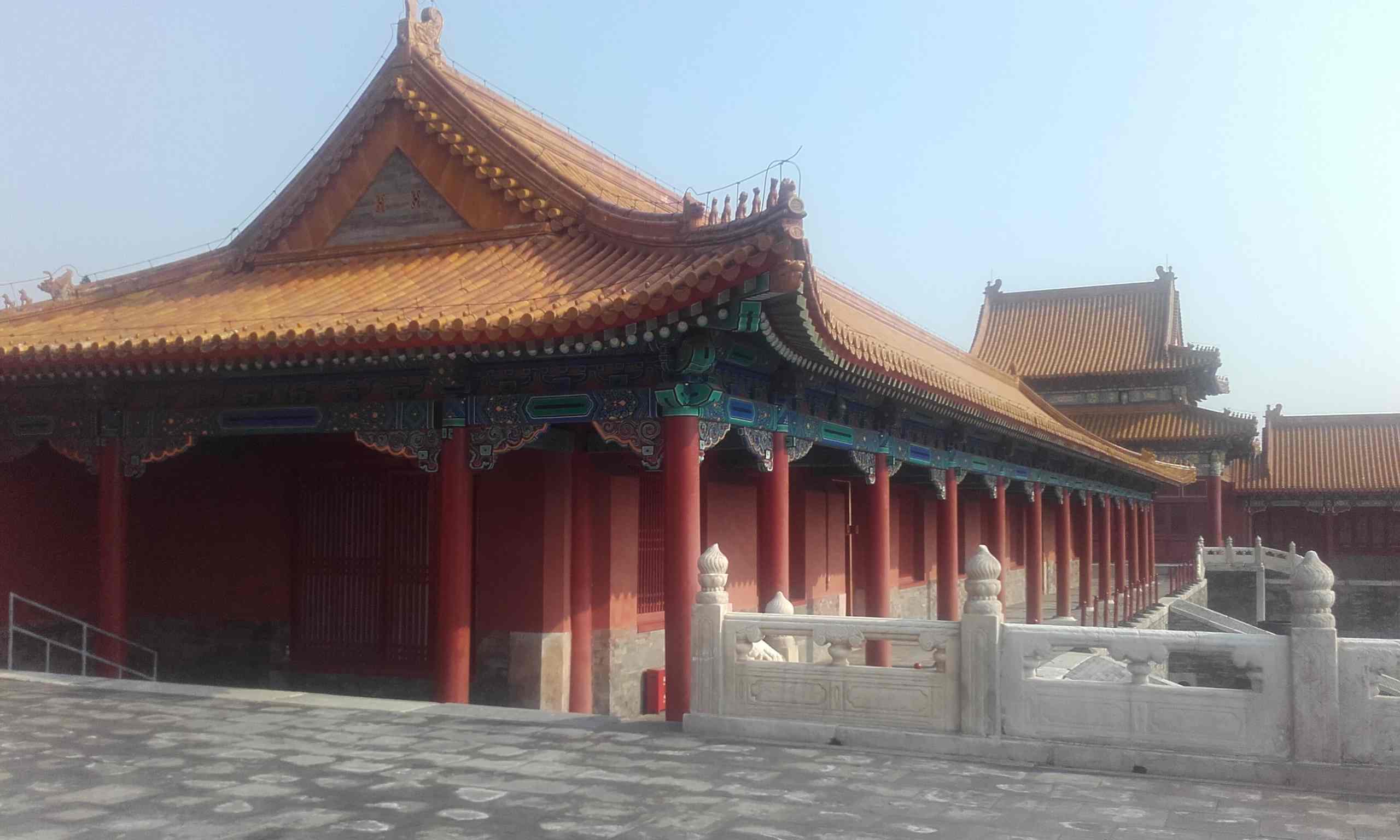
Beijing or northern capital has been one of the most exciting cities in the contemporary world and one of the world capitals today. It is a mix of traditional Chinese neighbourhoods and houses called hutong (胡同) and modern skyscrappers. Although the cultural heritage of Beijing consists of different architecture, historical remains and events –to mention Summer Palace, Tiantan or Temple of Heaven, Great Wall, Tiananmen Square, there is a place where everything started: Forbidden city.